Overview
There are a lot of AWR related scripts stored in $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin. I will focus on the most important ones.
Pitfall: You need a valid Diagnostic Pack license before you can use scripts like $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awr*.sql
The scripts are groupable by their filed of application. I will talk about each group later.
Performance Reports
Table: AWR Performance Report Scripts
| Script | Description |
| awrrpt.sql | RePorTs for current single instance database |
| awrrpti.sql | AWR RePorT for another dbid or instance (even RAC) |
awrgrpt.sql | AWR Global RePorT for current RAC |
| awrgrpti.sql | AWR Global RePorT for RAC another dbid, another instance |
Performance Reports Comparison
Table: AWR Performance Report Comparison Scripts
| Script | Description |
| awrddrpt.sql | AWR DateDiff RePorT for current single instance database |
| awrddrpi.sql | AWR DateDiff RePort for another dbid, another instance |
awrgdrpt.sql | AWR dateDiff RePorT for Global RAC View on current RAC |
| awrgdrpi.sql | AWR dateDiff RePort for Global RAC View for another dbid, another instance |
SQL Reports
Table: AWR SQL Report Scripts
| Script | Description |
| awrsqrpt.sql | AWR SQl statement RePorT for current single instance database |
| awrsqrpi.sql | AWR SQl statement RePorT for another dbid or instance |
AWR data movement
Table: AWR Data Movement Scripts
| Script | Description |
| awrextr.sql | export awr data using datapump |
| awrload.sql | import awr data using datapump |
Additional Scripts
Table: AWR Additional Scripts
| Script | Description |
| perfhubrpt.sql | Performance Hub Active Report |
| awrinpnm.sql | AWR INput NaMe |
| awrinput.sql | Get inputs for AWR reports |
| awrddinp.sql | Get inputs for AWR diff report (awrddrpi.sql) |
| awrgdinp.sql | Get inputs for AWR global diff reports (awrgdrpi.sql) |
Which script to use when?
At first sight those filenames seem to be random, but they aren’t.
There is a naming concept behind the ugly looking filenames. All files are limited to 8 characters without file extension. Sounds familiar? That is why there is a lot of abbreviation and it is not fully consistent.
Table: AWR filename abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Description |
| awr | automatic workload repository |
| rp, rpt | The word report is abbreviated as rp or rpt. rpt is used on default scope only when you cannot specify an instance |
| i | can select a specific instance (and dbid) |
| g | It is assuming you know that a Global view on data is only needed for RACs. |
| d | difference report, data comparisons of multiple reports |
| dd | difference report for single instance |
| gd | difference report for global views (rac) |
| sq | abbreviate sequel or sql |
| inp | input |
You can identify the scope by their names.
Table: AWR filename groups
| Script | Description |
| awr*rpt.sql | Generates report for the current db. Use this for single instances. It aggregates all available data from start-snapshot until including stop snapshot. |
| awr*rpi.sql | like awr*rpt.sql with extra option to select another dbid and/or a specific instance. Use this to watch a single instance of a Real Application Clusters (RAC) . The ability to select another dbid is crucial if you start moving around AWR data using awrextr.sql, awrload.sql, |
| awrgrpt*.sql | like awr*rpt.sql but specially to give a merged global view on a Real Application Cluster (RAC) . If you need an instance-by-instance view use awrrpti.sql instead |
| awrsq*rp*.sql | SQL Statement RePortTs |
| awr*drp*.sql | Compares reports |
| awr*inp*.sql | Get input for the according scripts with similar name. Use this script do define variables before running the actual script. Use this for automation. |
Performance Reports (awr*rpt*.sql)
Try to use the Oracle Enterprise Manager if possible. All these reports have similar usage and output. I am only showing one of them. Some of them are not asking for dbid or instance. awrrpt.sql, awrrpti.sql, awrgrpt.sql, awrgrpti.sql
Example: Starting a performance report script from sqlplus
| SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrgrpti.sql |
Oracle recommends using html for RAC and comparison because it has a nicer format. I like formatted ascii but active-html has nice charts and graphs. This includes the Performance Hub active report.
Unfortunately, these active-html does not work reliably so I often just pick text and leave the unusable charts alone. Default value is text.
Example: setting report type in performance report script
Enter value for report_type: active-html
You see this question only in *i.sql scripts. It asks for dbid and number of instances to include in report.
Example: setting dbid and instance_number in performance report script
Instances in this Workload Repository schema
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
DB Id Inst Num DB Name Instance Host
———— ———- ——— ———- ——
3180801162 1 ORCL orcl1 oelrac01.local
3180801162 2 ORCL orcl2 oelrac02.local
* 1313517682 1 CWDB cwdb oel76.local
Enter value for dbid: 3180801162
Enter value for instance_numbers_or_all: 1
Using instances all (default ‚ALL‘)
You see this screen in every type of interactive report when snap_ids are not defined.
This page contains filtered information from dba_hist_snapshot (list AWR snapshots). It asks you how many days of snapshots you want to display to choose the right snap_ids .
Example: enter range of snaps to display for selection in performance report script
| Enter value for num_days: 1 |
Example: setting begin_snap, end_snap in performance report script
Listing the last day’s Completed Snapshots
DB Name Snap Id Snap Started Snap Level
———— ———- —————— ———-
ORCL 21375 06 May 2020 18:00 1
21376 06 May 2020 18:15 1
21377 06 May 2020 18:30 1
21378 06 May 2020 18:45 1
Enter value for begin_snap: 21376
Enter value for end_snap: 21377
Example: setting output filename in performance report script
| Enter value for report_name: |
| Using the report name awrrpt_rac_21376_21377.html |
If you accept the default it will be created in in userhome
Tip: If you accept the default name it will be created in directory you are in when starting sqlplus. Maybe ~ or $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin
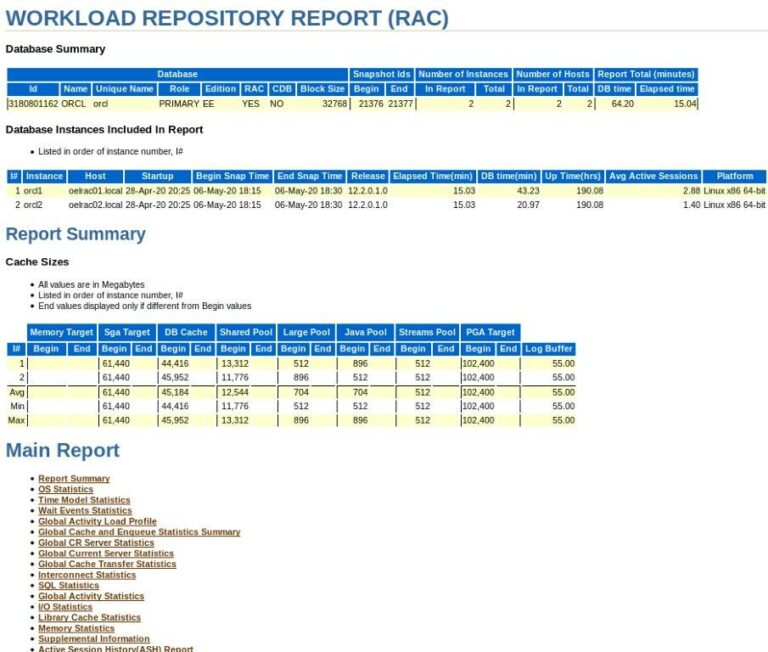
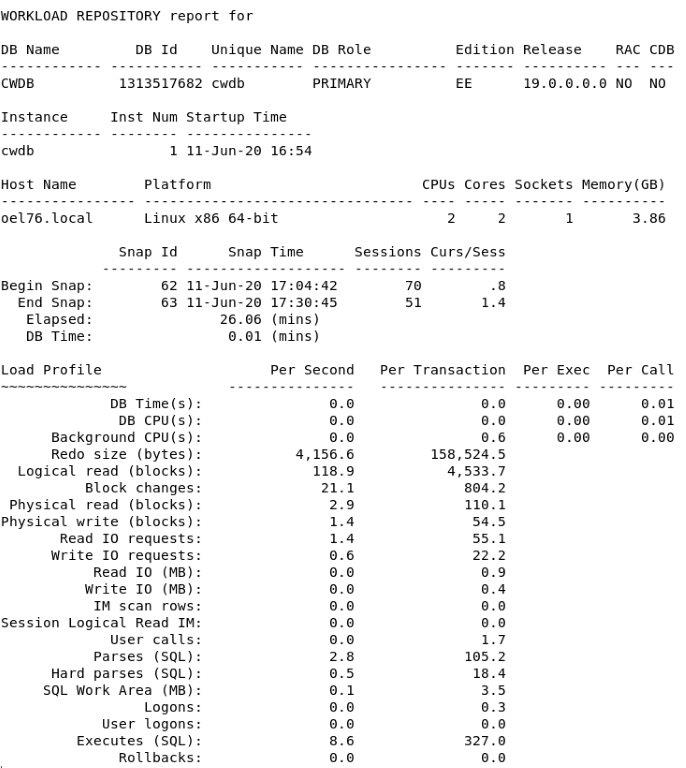
Performance Report Comparison (awr*drp*.sql)
You can use this to compare different pairs of snapshots of same instance or even different instances. Comparing snapshots of different instances or databases is one of the use cases for moving AWR data.
Example: Starting performance report comparison script from SQLPlus
| SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrgdrpi.sql |
Tip: Use html if possible because it is easier to view than text reports
Example: enter report_type in report comparison script
| Enter value for report_type: html |
Example: enter dbid in report comparison script
Instances in this Workload Repository schema
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
DB Id Inst Num DB Name Instance Host
———— ———- ——— ———- ——
3180801162 1 ORCL orcl1 oelrac01.local
3180801162 2 ORCL orcl2 oelrac02.local
* 1313517682 1 CWDB cwdb oel76.local
Database Id and Instance Number for the First Pair of Snapshots
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Enter value for dbid: 1313517682
Tip: You must enter value for dbid. If you just accept the defaults it will fail
Example: enter instance_number in report comparison script
| Enter value for instance_numbers_or_all: 1 |
Example: range of snaps to display in report comparison script
Enter value for num_days: 1
Listing the last day’s Completed Snapshots
DB Name Snap Id Snap Started Snap Level
———— ———- —————— ———-
CWDB 62 11 Jun 2020 17:04 1
63 11 Jun 2020 17:30 1
64 11 Jun 2020 18:00 1
65 11 Jun 2020 18:30 1
Example: enter begin_snap, end_snap in report comparison script
Specify the First Pair of Begin and End Snapshot Ids
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Enter value for begin_snap: 62
Enter value for end_snap: 63
Now the same questions as above for the second snapshot. I will truncate the outputs a little.
Example: enter snapshot information for second pair in report comparison script
Instances in this Workload Repository schema
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
DB Id Inst Num DB Name Instance Host
———— ———- ——— ———- ——
3180801162 1 ORCL orcl1 oelrac01.local
3180801162 2 ORCL orcl2 oelrac02.local
* 1313517682 1 CWDB cwdb oel76.local
Database Id and Instance Number for the Second Pair of Snapshots
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Enter value for dbid: 1313517682
Enter value for instance_numbers_or_all2: 1
Enter value for num_days2: 1
Enter value for begin_snap2: 64
Enter value for end_snap2: 65
Example: enter report name in report comparison script
| Enter value for report_name: |
| Using the report name awrracdiff_1st_62_2nd_64.html |
Example: HTML Report of Single Instance Compare Period
To be honest, I used the RAC report to accomplish this result. It is just the same but asking for instance number which always 1 in single instances.
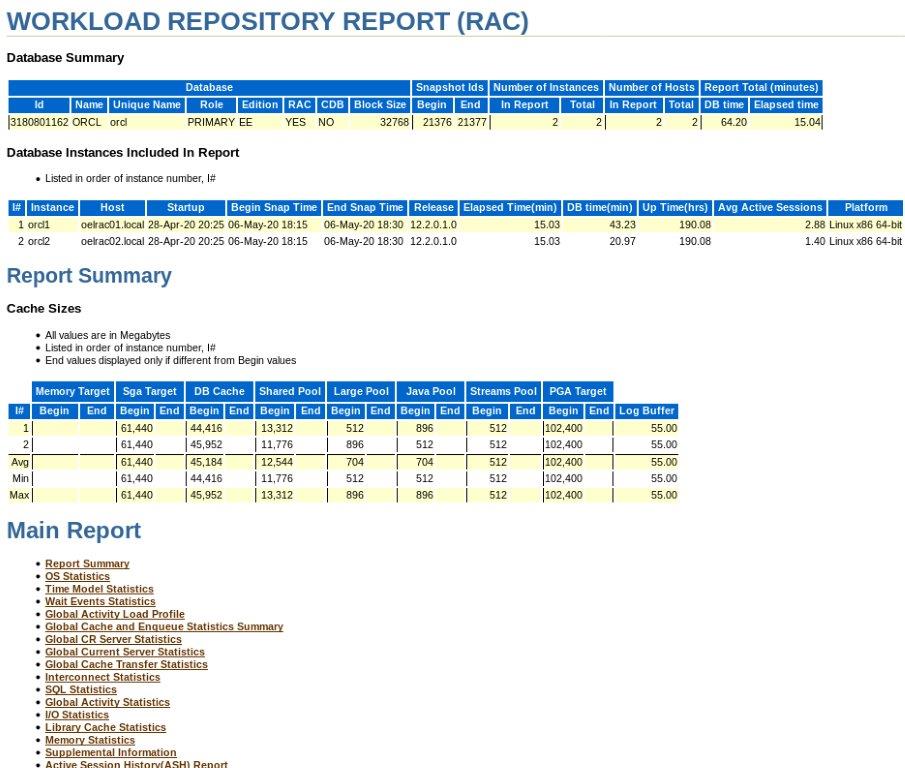
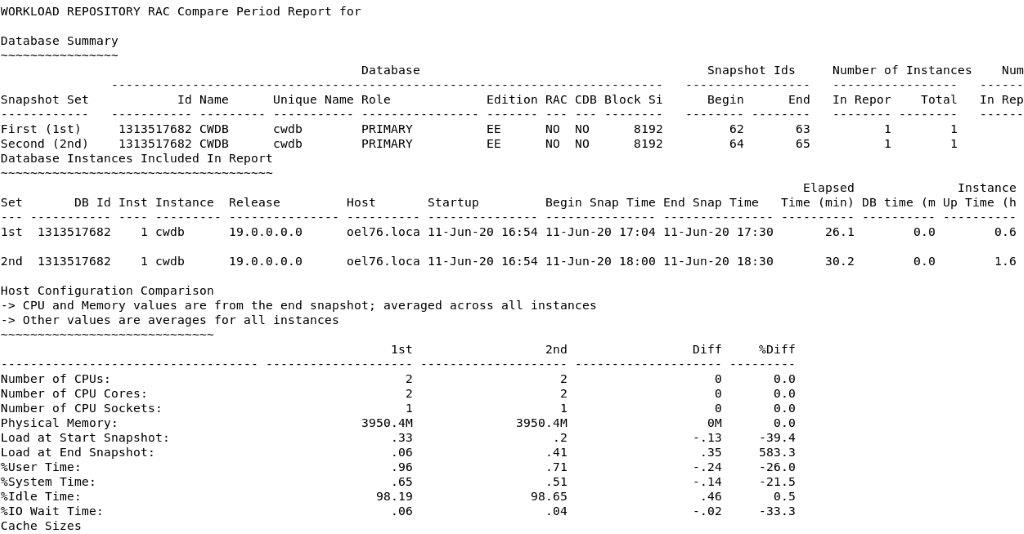
Workload-Repository RAC Compare Period Report
It is just too wide to fit on my screen without line break.
SQL Statement Reports (awrsqrp*.sql)
Example: Starting SQL statement report script from sqlplus
| SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrsqrpi.sql |
Example: enter report_type in SQL statement report script
| Enter value for report_type: html |
Example: choose dbid and instance where to search sql_id
Instances in this Workload Repository schema
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
DB Id Inst Num DB Name Instance Host
———— ———- ——— ———- ——
3180801162 1 ORCL orcl1 oelrac01.local
3180801162 2 ORCL orcl2 oelrac02.local
* 1313517682 1 CWDB cwdb oel76.local
Enter value for dbid: 1313517682
Enter value for inst_num: 1
Example: range of snaps to display in SQL statement report script
Enter value for num_days: 2
Listing the last 2 days of Completed Snapshots
Instance DB Name Snap Id Snap Started Snap Level
———— ———— ———- —————— ———-
cwdb CWDB 62 11 Jun 2020 17:04 1
63 11 Jun 2020 17:30 1
64 11 Jun 2020 18:00 1
65 11 Jun 2020 18:30 1
Example: enter begin_snap, end_snap in SQL statement report script
| Enter value for begin_snap: 62 |
| Enter value for end_snap: 63 |
This is a new screen exclusive to this report.
You need to know a specific dbid first to answer the question. Look at one of the reports for sql_id or lookup in database (for example: v$session)
Example: enter sqlid to be found in dbid
Specify the SQL Id
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Enter value for sql_id: 22356bkgsdcnh
SQL ID specified: 22356bkgsdcnh
Listing all available Container DB Ids for SQL Id 22356bkgsdcnh
Container DB Id Container Name
—————– ————–
* 1313517682 cwdb
Using Container DB Id 1313517682
Same screen, new filename.
Example: enter report name in SQL statement report script
| Enter value for report_name: |
| Using the report name awrsqlrpt_1_62_63.html |
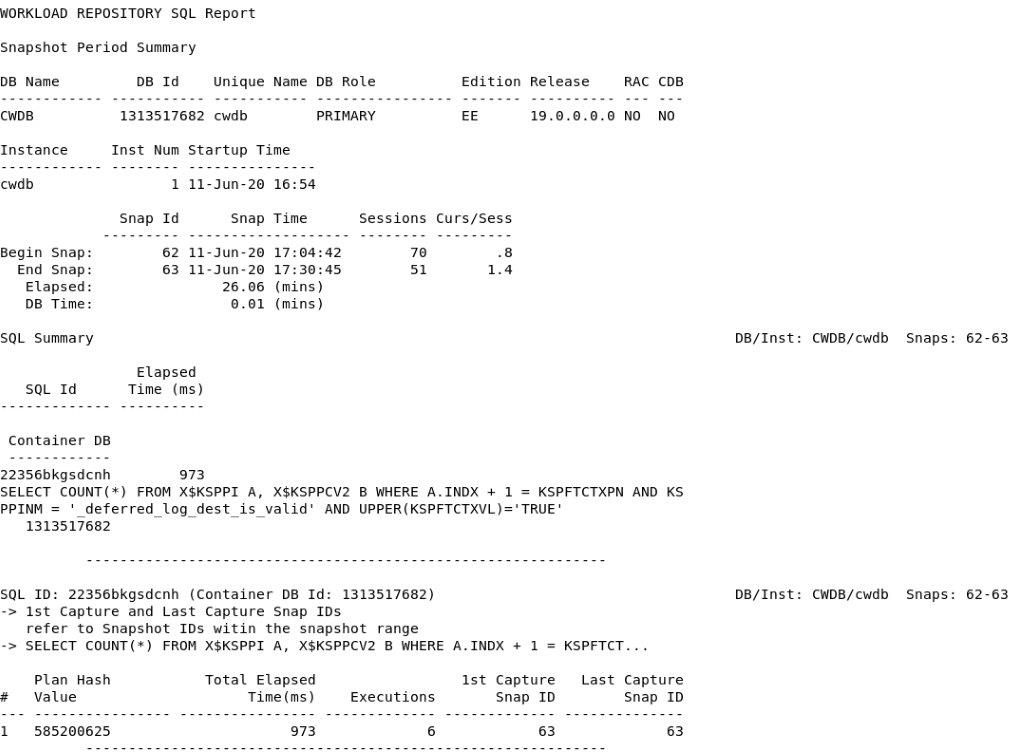
Example: HTML SQL Report
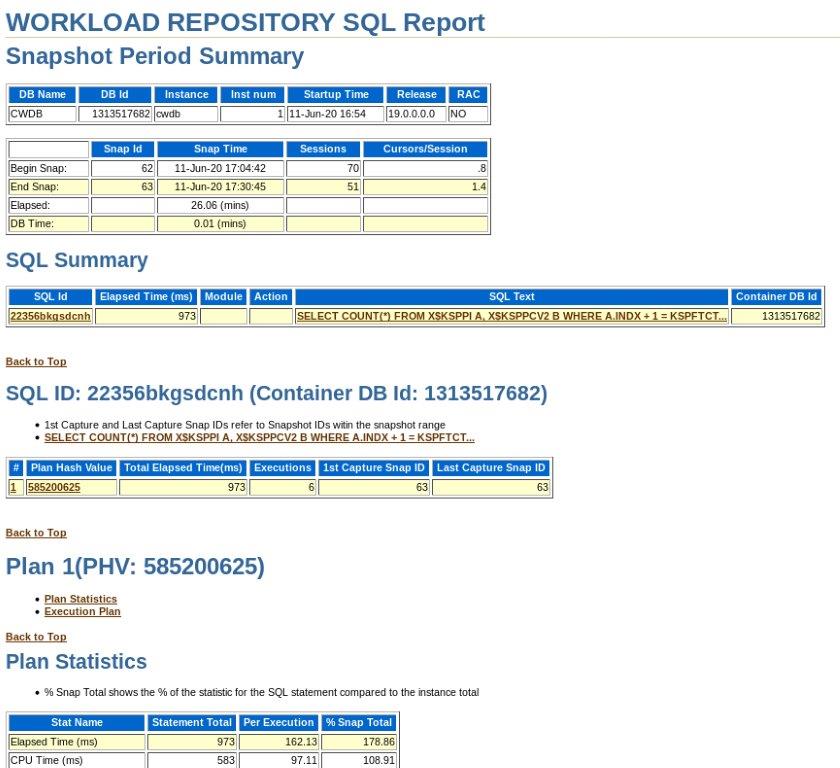
Example: TEXT SQL Report
Moving AWR Data (awrextr.sql, awrload.sql)
There are special cases when you need to move AWR data from one database to another:
- The performance analyst might not be able to access the source and needs a dump
- AWR data needs to be stored externally
- want to compare AWR Reports of different databases / instances
- want to compare very old snapshots (not in AWR anymore)
- You want an Automatic Workload Repository Warehouse but do not have a CloudControl available
Tip: You cannot export/import AWR data into the same database. Thus, you cannot use this to backup/restore AWR data of your database.
awrextr.sql
Preparation
Export / Import works like datapump. You need to define a directory first.
Example: create datapump directory for AWR exports
| SQL> create or replace directory awrtransfer as ‚/awrtransfer/data/‘; |
export
If you do not predefine variables the script will ask you for it. You must run this as sysdba.
Example: Starting AWR Export Script in interactive mode from SQLPlus
| SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrextr.sql |
In this special case I want to export data from CWDB single instance. If you are exporting RAC data, it automatically selects all instances for you.
Example: selecting dbid to export in awrexport script
DB Id DB Name Host
———— ———— ————
* 1313517682 CWDB oel76.local
3180801162 ORCL oelrac01.local
3180801162 ORCL oelrac02.local
Enter value for dbid: 1313517682
Example: selecting snapshot range to display in awrexport script
Enter value for num_days: 2
DB Name Snap Id Snap Started
———— ——— ——————
CWDB 62 11 Jun 2020 17:04
63 11 Jun 2020 17:30
64 11 Jun 2020 18:00
65 11 Jun 2020 18:30
Example: selecting snapshot range to export in awrexport script
| Enter value for begin_snap: 62 |
| Enter value for end_snap: 66 |
Example: selecting datapump directory for export in awrexport script
Directory Name Directory Path
—————————— ————————————-AWRTRANSFER /awrtransfer/data/
DATA_PUMP_DIR /u01/app/oracle/admin/cwdb/dpdump/
Choose a Directory Name from the above list (case-sensitive).
| Enter value for directory_name: AWRTRANSFER |
Note how the filename extensions will be appended automatically. No need to define it. If you do not define a filename prefix it will just use the snap values in name.
Example: accept default value as filename
| Enter value for file_name: |
| Using the dump file prefix: awrdat_62_66 |
| datafile: /awrtransfer/data/awrdat_62_66.dmp |
| logfile: /awrtransfer/data/awrdat_62_66.log |
Scripting
Example: define variables before calling awrextr.sql in sql file
| awrextr-wrapper.sql |
| define dbid=1313517682; |
| define begin_snap=62; |
| define end_snap=63; |
| define num_days=1; |
| define directory_name=’AWRTRANSFER‘; |
| define file_name=’awrexp_62_63′; |
| @?/rdbms/admin/awrextr.sql |
You can even wrap this as an heredoc in bash. Maybe I will add another post for automating this task.
Example: pass variables for awrextr.sql in shell script as heredoc
| awrextr-wrapper.sh |
| #!/bin/bash |
| dbid=1313517682; |
| begin_snap=62; |
| end_snap=63; |
| directory_name=’AWRTRANSFER‘; |
| file_name=’awrexp_62_63′; |
| # start awrextr from bash |
| sql_awr=`sqlplus -silent /nolog <<EOSQL |
| connect / as sysdba |
| whenever sqlerror exit sql.sqlcode |
| spool ‚$spoolfile‘ |
| define dbid=’$dbid‘; |
| define begin_snap=${begin_snap}; |
| define end_snap=${end_snap}; |
| define num_days=1; |
| define directory_name=’${directory_name}‘; |
| define file_name=’${dumpfile}‘; |
| @?/rdbms/admin/awrextr.sql |
| spool off |
| exit; |
| EOSQL` |
awrload.sql
Preperation
Export / Import works like datapump. You need to define a directory first.
Example: create datapump directory for AWR imports
| SQL> create or replace directory awrtransfer as ‚/awrtransfer/data/‘; |
Data will be Imported into a dedicated STAGING Area before it will be transferred to SYSAUX Tablespace and SYS User Schema.
You may create STAGING_TABLESPACE and STAGING_TEMP_TABLESPACE manually before importing. It is possible to use existing tablespaces too.
Example: create custom staging tablespaces for awr import
| SQL> create tablespace AWR_STAGE datafile size 1G autoextend on maxsize unlimited; |
| SQL> create temporary tablespace AWR_TEMP tempfile size 1G autoextend on maxsize 10G; |
Do not create a STAGING_USER. It will be created automatically and must not exist.
import
Tip: You cannot import AWR data into the same database you exported from. You will see ORA-20303. Import to another dbid.
Example: Starting AWR Import Script in interactive mode from SQLPlus
| SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrload.sql |
Example: selecting datapump directory for export in awrimport script
Directory Name Directory Path
—————————— ————————————-AWRTRANSFER /awrtransfer/data/
DATA_PUMP_DIR /u01/app/oracle/admin/cwdb/dpdump/
Choose a Directory Name from the above list (case-sensitive).
Enter value for directory_name: AWRTRANSFER
It automatically appends .dmp to the given prefix.
Example: enter filename to use without extension
| Enter value for file_name: awrdat_orcl_20_27 |
| Loading from the file name: awrdat_orcl_20_27.dmp |
The schema-name AWR_STAGE is the default suggestion. This Schema may not exist in target database.
Example: accept default schema name to use for import
| Staging Schema to Load AWR Snapshot Data |
| Enter value for schema_name: |
| Using the staging schema name: AWR_STAGE |
You can use any existing tablespace for import. I prefer using a dedicated tablespace to isolate the date in case of errors.
Example: enter tablespace name to use for import
TABLESPACE_NAME CONTENTS DEFAULT TABLESPACE
———————- ——————— —————
AWR_STAGE PERMANENT
SYSAUX PERMANENT *
Enter value for default_tablespace: AWR_STAGE
You can use any existing temporary tablespace.
Example: enter temporary tablespace name to use for import
TABLESPACE_NAME CONTENTS DEFAULT TEMP TABLESPACE
———————- ——————— ———————–
TEMP TEMPORARY *
Enter value for temporary_tablespace: TEMP
After import, the created User AWR_STAGE will be dropped. Tablespaces will remain.
Example: important screen output of awrload.sql
| … Creating AWR_STAGE user |
| datafile: /awrtransfer/data/awrdat_orcl_20_27.dmp |
| logfile: /awrtransfer/data/awrdat_orcl_20_27.log |
| … Dropping AWR_STAGE user |
Example: dba_hist_snapshot output with imported data
| SQL> select dbid, instance_number INST, snap_id, snap_level, |
| to_char(begin_interval_time,’yyyy.mm.dd hh24:mi:ss‘) snap_start, |
| error_count ERR, |
| — 19c only |
| decode (SNAP_FLAG, 0, ‚automatic‘, |
| 1, ‚manual plsql‘, |
| 2, ‚imported‘, |
| 4, ‚pack-was-not-enabled‘) CREATION |
| from DBA_HIST_SNAPSHOT; |
| DBID INST SNAP_ID LVL SNAP_START ERR CREATION |
| ———- —- ———- — ——————- — ————- |
| 1313517682 1 56 1 2020.06.06 21:32:16 0 automatic |
| 1313517682 1 44 1 2020.06.04 17:00:50 0 automatic |
| 1313517682 1 42 1 2020.06.04 15:13:44 0 automatic |
| 1313517682 1 45 1 2020.06.04 18:00:04 0 automatic |
| 3250804769 2 21362 1 2020.05.06 14:30:44 1 imported |
| 3250804769 2 21373 1 2020.05.06 17:15:25 1 imported |
| 3250804769 1 21358 1 2020.05.06 13:30:30 1 imported |
| 3250804769 1 21359 1 2020.05.06 13:45:32 1 imported |
Columns explained
SNAP_LEVEL – Parameter STATISTICS_LEVEL when snap was taken. 1 = TYPICAL 2 = ALL
ERROR_COUNT – this is new in 19c. Reporting will still work with minor glitches or missing information.
SNAP_FLAG – this in new in 19c. It shows how data was collected.
In this example I wanted to show you various possibilities. The first lines with dbid 1313517682 were automatically created in my single instance named CWDB. You already know them from the example above. Data was collected by default AWR job.
The data with dbid 3250804769 was imported using AWR scripts above. You can see it is even possible to import and analyse AWR data coming from RAC into a single instance.
If the source was Oracle Hardware (like Exadata) it will also show those Exadata values in reports created on another database.
Example: Existence of Exadata values in report created by moved data

awrload-wrapper.sql |
| define directory_name=’AWRTRANSFER‘; |
| define file_name=’awrexp_62_63′; |
| define schema_name=’AWR_STAGE‘; |
| define default_tablespace=’AWR_STAGE‘; |
| define temporary_tablespace=’AWR_TEMP‘ |
| @?/rdbms/admin/awrload.sql |
You can even wrap this as an heredoc in bash. Maybe I will add another post for automating this task.
Example: pass variables for awrload.sql in shell script as heredoc
awrload-wrapper.sh |
| #!/bin/bash |
| directory_name=’AWRTRANSFER‘; |
| dumpfile=’awrexp_62_63′ |
| stag_usr = ‚AWR_STAGE‘; |
| stag_tbs= ‚AWR_STAGE‘; |
| stag_tmp= ‚AWR_TEMP‘; |
| awr_load=`sqlplus -silent /nolog <<EOSQL |
| connect / as sysdba |
| whenever sqlerror exit sql.sqlcode |
| spool ‚$spoolfile‘ |
| define directory_name=’$directory_name‘; |
| define file_name=’$dumpfile‘; |
| define schema_name=’$stag_usr‘; |
| define default_tablespace=’$stag_tbs‘; |
| define temporary_tablespace=’$stag_tmp‘; |
| @?/rdbms/admin/awrload.sql |
| spool off |
| exit; |
| EOSQL` |
Additional Scripts
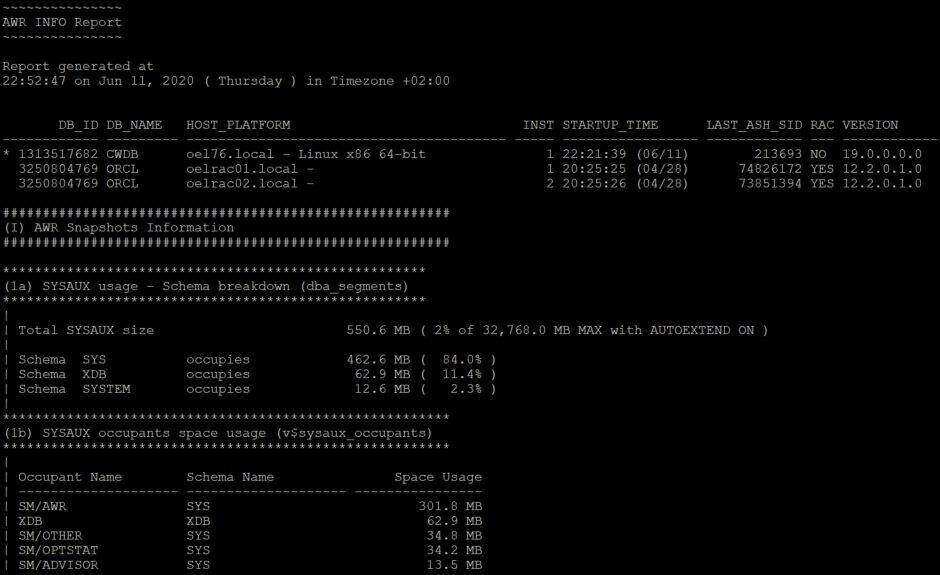
awrinfo.sql
Just collects a bunch of AWR information. We already queried some information ourselves above, but this is the full content.
Example: Starting awrinfo script from SQLPlus
| SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrinfo |
There is no other option than creating a text file.
Example: TEXT awrreport.txt in bash
Performance Hub Active Report (perfhubrpt.sql)
This is not a traditional AWR Report but this Report will be included in 19c when you choose active-html as output format. It is such a good report I just want to tell it here. It looks like the report you know from CloudControl or EM Express but you cannot „move“ the timerange slider.
Example: Starting Performance Hub Report from SQLPlus
| SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/perfhubrpt.sql |
Example: entering report level in Performance Hub Report
| Please enter report level [typical]: |
Table: PerformanceHubReport Levels
| Level | Description |
| basic | include tab contents but no further details |
| typical | include tab contents with details for top SQL statements (default) |
| all | include tab contents with details for all SQL statements |
Note the newly added Type column. It contains useful information about the data available.
Example: enter dbid of database for Performance Hub Report Script
Available Databases and Instances.
The database with * is current database
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
DB Id DB Name AWR Data Source Type
------------ ------------ ------------------------ -----------------
* 1313517682 CWDB CWDB NON_CDB
3250804769 ORCL ORCL IMPORTED, RAC
Specify the database ID
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Please enter database ID [1313517682]:
Example: enter instance_number Performance Hub Report script
Instance Number will be automatically selected for single instances.
Specify the Instance Number
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Single Instance Database. Please press Enter
Note: If the dbid selected was imported only AWR data is available
This is the range you will see in time range slider later. There are various options here to define the time range. absolute and relative notations are available here.
Example: enter start_time, end_time in Performance Hub Report script
Default Start Time Default End Time Oldest Available Snapshot
——————- ——————- —————————-
06/11/2020 22:28:17 06/11/2020 22:33:17 06/04/2020 15:13:43
Please enter start time [06/11/2020 22:28:17]: -01:00
Please enter end time [06/11/2020 22:33:17]:
Example: enter report name in Performance Hub Report script
Specify the Report Name
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Please enter report name [perfhub_rt_06112233.html]:
Image: Performance Hub Report generated with perfhubrpt.sql
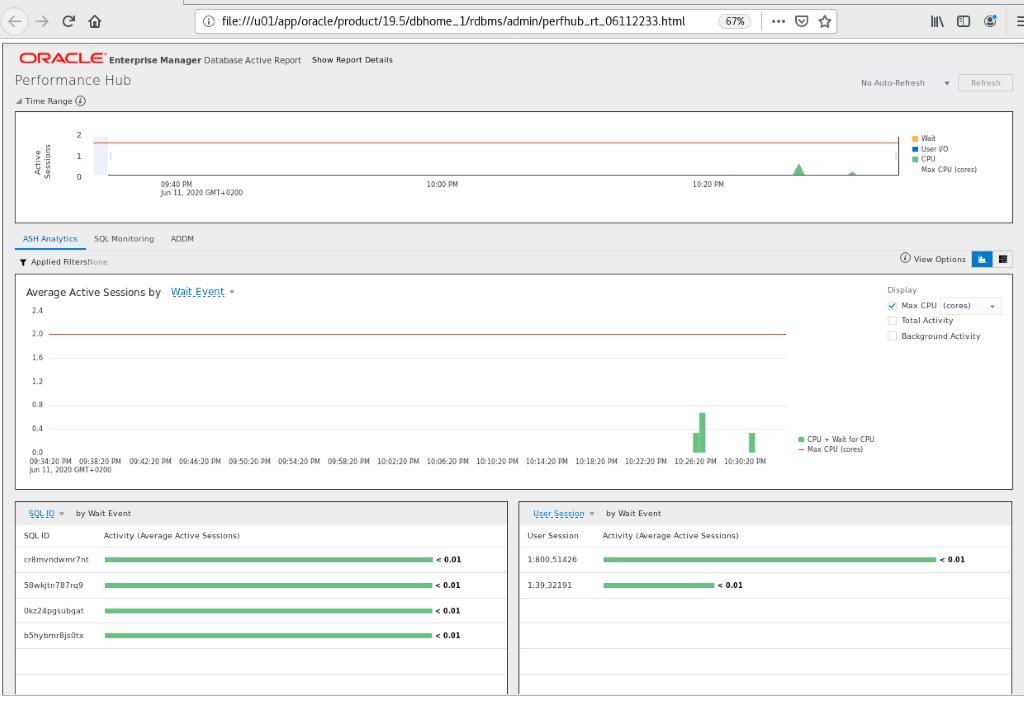
Looks very similar to what you see on EM Express or CloudControl. Active HTML allows some dynamics, but the time range is not adjustable within these reports.
Summary
- start using AWR. Only if you know what is going on inside your database you can adjust the sails
- care about licensing to avoid penalty fees
- if you are not entitled to use AWR use STATSPACK at least
- configure AWR to the granularity you need
- remove unneeded data automatically
- Cloud Control is much better than EM Express
- some use cases might need pre-made scripts
- simply start using it. you will become more and more confident
First Part – Oracle Automatic Workload Repository Part1 : Getting Startet







